Super Glow Stars
Pick your moisturizer
No matter your skin type or concern, we have just the right moisturizer for you!



Skin type
Bodycare Spotlight
Dive into our latest launches
What does your skin need help with?
Most Beautiful Wall
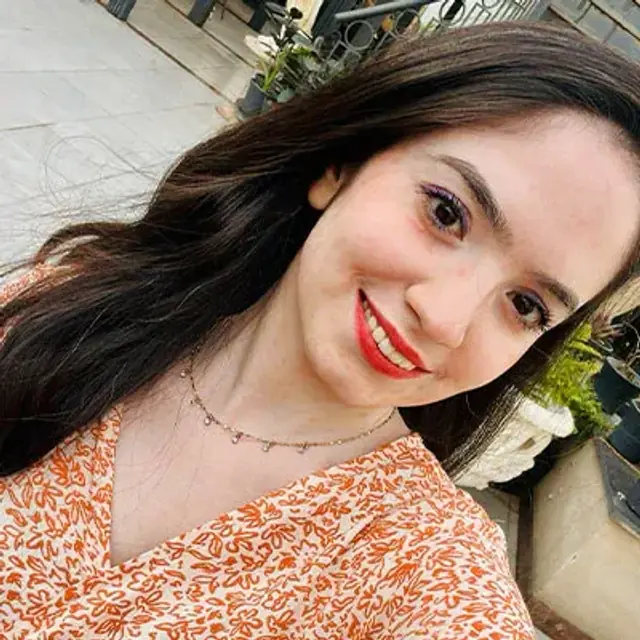

ANMOL ARORA | CITY: DELHI
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Celebrating her Vitiligo, her confidence and the perfect red lip balm!

Most Beautiful Wall
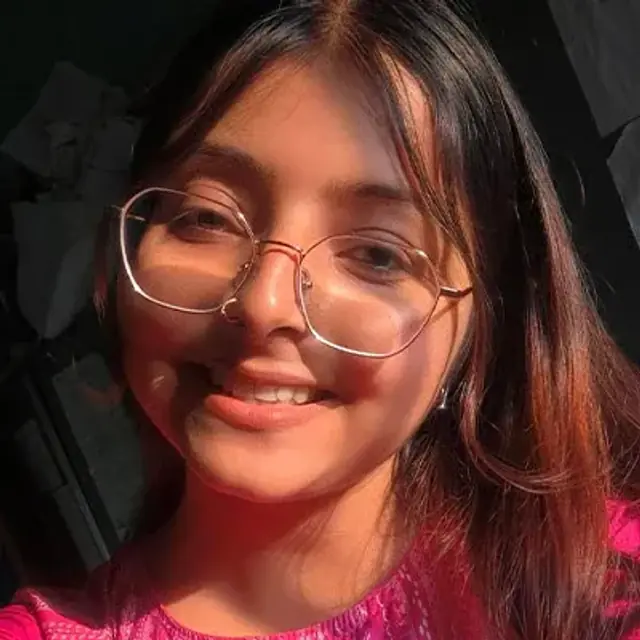

ANISHA BHARDWAJ | CITY: LAKHIMPUR
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Celebrating her quirks, her favourite book and the Glow Sunscreen!

Most Beautiful Wall
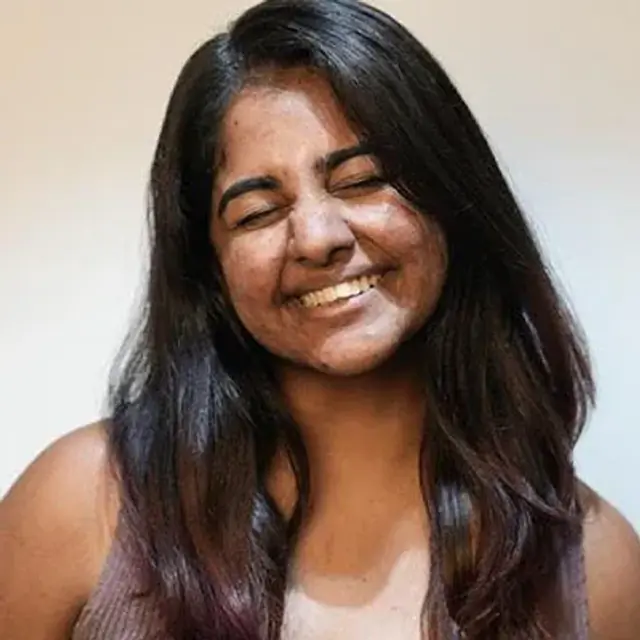

SHREYA | CITY: MUMBAI
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Owning her acne scars like a boss and her most trusted Mattifying Sunscreen

Most Beautiful Wall
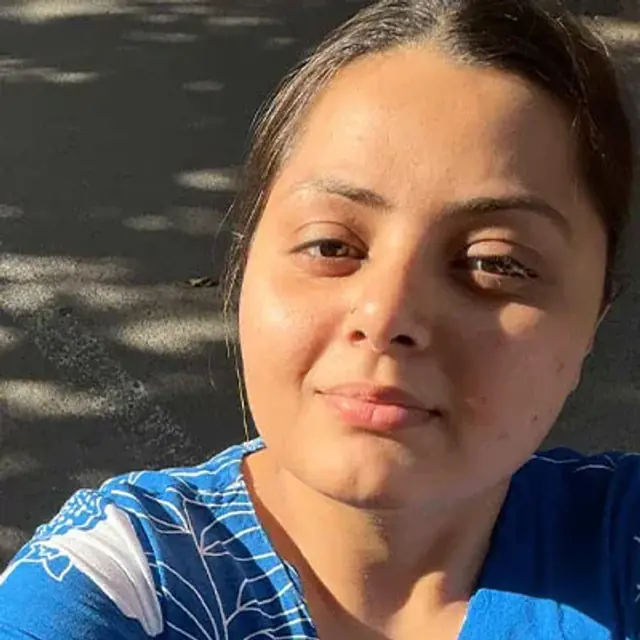

NEET | CITY: GUWAHATI
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
A morning walk, showing off her natural skin and marks and the Super Glow Face Wash

Most Beautiful Wall
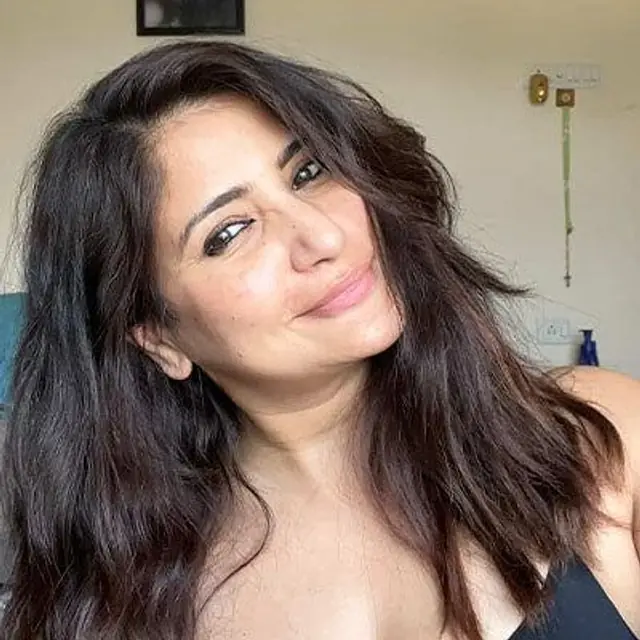

SUNI | CITY: MUMBAI
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Her daughters' love, skin that ages gracefully & skincare that loves her back.

Most Beautiful Wall
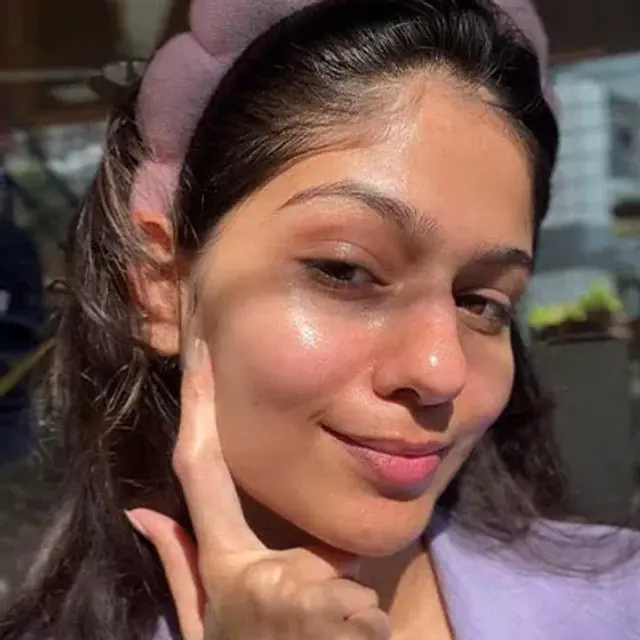

ASMI | CITY: PUNE
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
The morning sun, her mom's parathas & the nano - Vitamin C in the Super Glow Moisturizer

Most Beautiful Wall
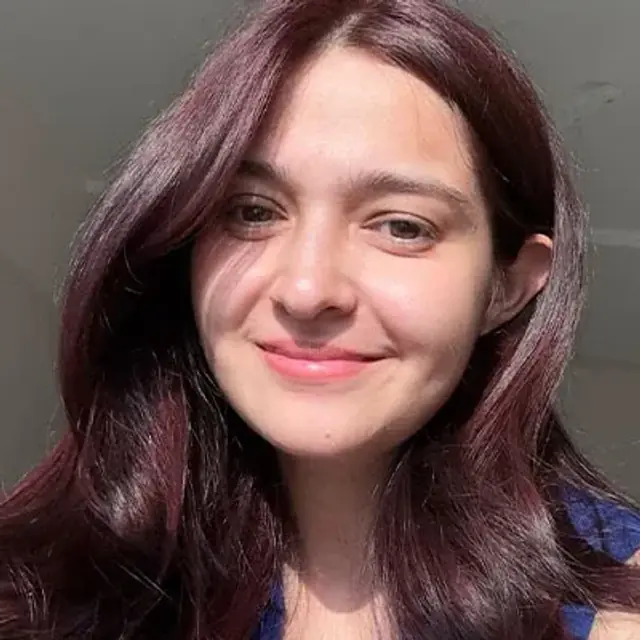

KAVITA | CITY: MUMBAI
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Ditching the makeup, Sunday mornings & her fav purple mask!

Most Beautiful Wall
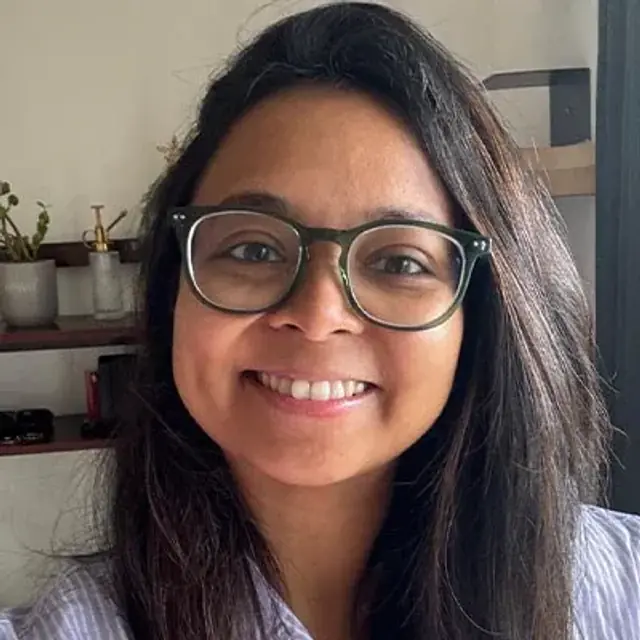

JANICE | CITY: JAIPUR
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Never fitting into other's idea of "perfect" & her OG clear Lip Balm!

Most Beautiful Wall
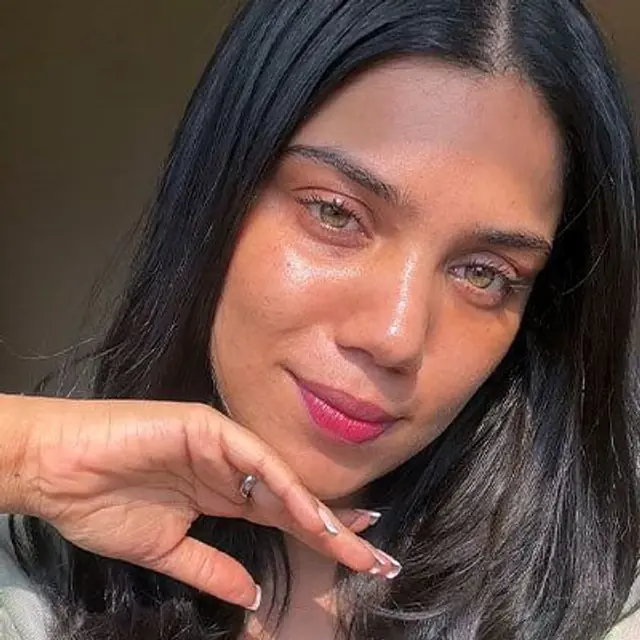

MOUSSHMI | CITY: MUMBAI
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Celebrating her glowy skin, her unique eyes & the Dewy Sunscreen

Most Beautiful Wall
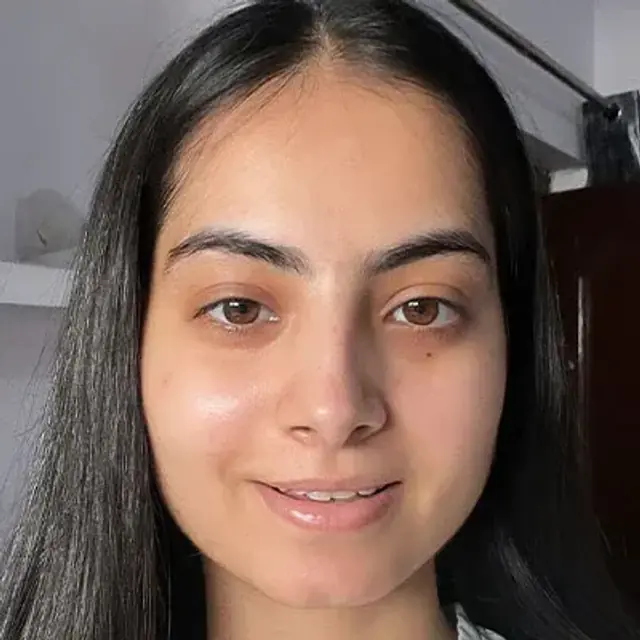

MANI | CITY: GANGANAGAR
What makes her glow, unfiltered?
Her favourite snack, a lit-from-within glow & the Glow Sunscreen
Get featured here! Snap a selfie, tag
@foxtaleskin, and use #MostBeautifulWall
Peak into Foxtale HQ
Our Product Playbook
High-Performing
Visible results from the 1st use

Skincare shows results when you're consistent. Visible improvement everyday improves consistency.
Our fast-acting formulas and unique ingredient story ensures visible improvement from the very first use.
Innovative
Unique Dermal Delivery Systems
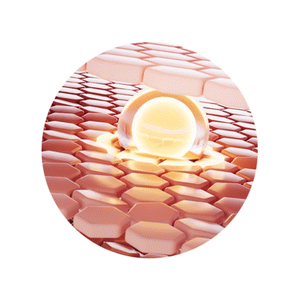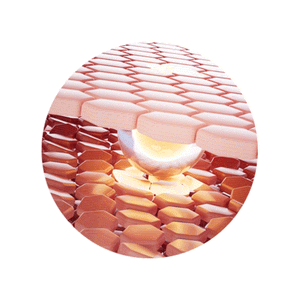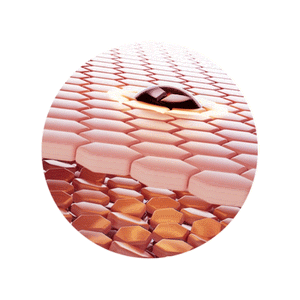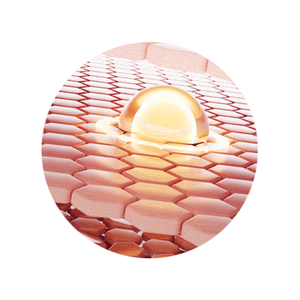
Different concerns show up in different layers of skin
Our unique Active Delivery Systems ensure the actives reach the necessary layers and tackle skin concerns like increased melanin production, dehydration, collagen loss and wrinkles.
Safe
Boosted Skin Health Enhancers

Healthy Skin = Glowing Skin
Our products are formulated with skin health enhancers that complement actives for targeted solutions.
They increase skin's moisure levels and support barrier function to give you a lit-from-within glow.
01
03





















































